As technology continues to advance, you’ve probably heard a lot of talk about 5G and how it’s going to change the way we connect. But what exactly is the difference between 4G and 5G? And how does this shift impact you? Let’s break it down in a simple way.
Speed: A Major Upgrade When 4G came along, it was a game-changer for mobile internet. Download speeds were fast enough for streaming HD videos, loading websites quickly, and handling our growing app usage. However, 5G takes speed to the next level. Think of 4G as driving on the freeway—fast, but with some limits. 5G is more like a high-speed train, designed to handle huge amounts of data at much faster speeds. In practical terms, this means you could download an entire movie in seconds instead of minutes.

Latency: Faster Response Times Latency refers to how long it takes for your device to communicate with the network. With 4G, you might experience a slight delay when loading a webpage or during a video call. 5G, on the other hand, reduces that delay to almost zero. This is crucial for activities like online gaming, live streaming, or video conferencing, where even a small lag can be frustrating.
Capacity: More Devices, Less Congestion 4G networks, while robust, can become congested when too many devices connect at once. This is especially noticeable in crowded areas, such as concerts or sports events. 5G addresses this issue by increasing network capacity, allowing many more devices to connect simultaneously without slowing down performance. This improvement is critical as the number of connected devices continues to rise.
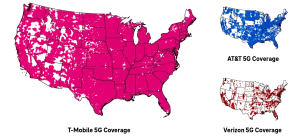
Coverage: A Work in Progress While 4G offers broad coverage, 5G is still in its early stages of rollout. Currently, 5G is most effective in urban areas where the necessary infrastructure has been built. The technology behind 5G relies on higher-frequency signals, which can provide faster speeds but don’t travel as far or penetrate obstacles as easily as 4G signals. As a result, 5G is often used in combination with 4G to ensure continuous coverage, especially in more rural or suburban areas. See T Mobile’s 5G Map here or see Verizon’s map here.
Conclusion: A Step Toward the Future While 4G has served us well over the past decade, 5G represents a significant advancement in mobile technology. The benefits of faster speeds, lower latency, and greater network capacity will pave the way for innovations across various industries. However, it will take time for 5G to be fully integrated everywhere. For now, both 4G and 5G will coexist, each offering reliable connectivity depending on location and network availability.
All the best,
Your Suburban Technology Team